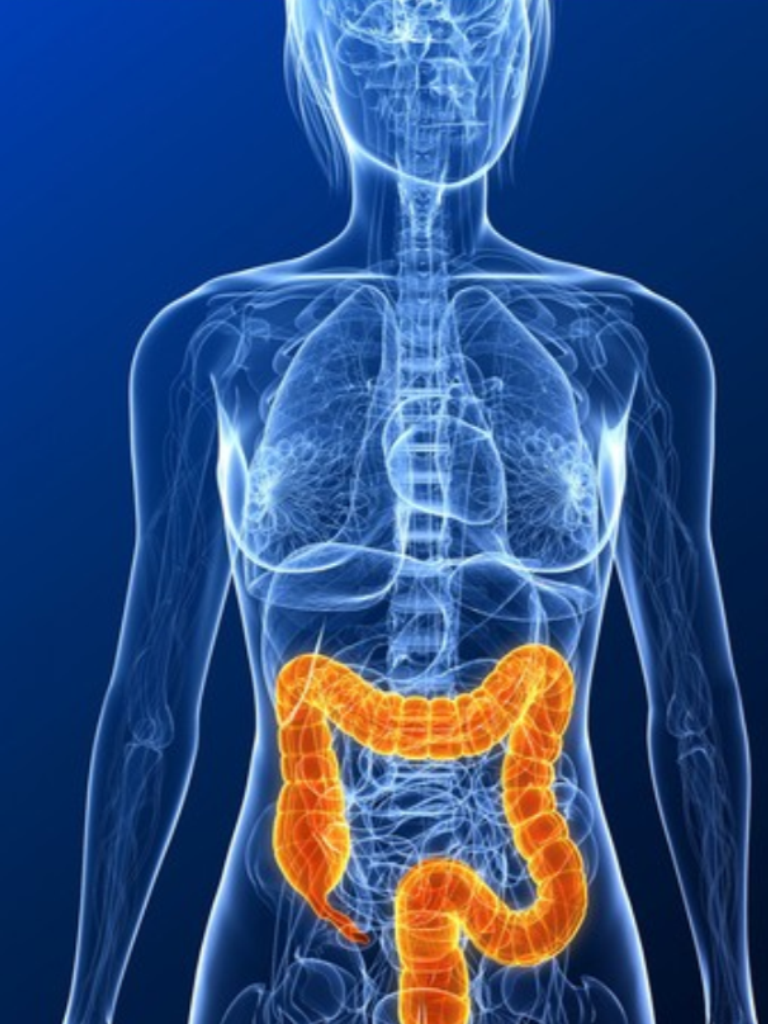
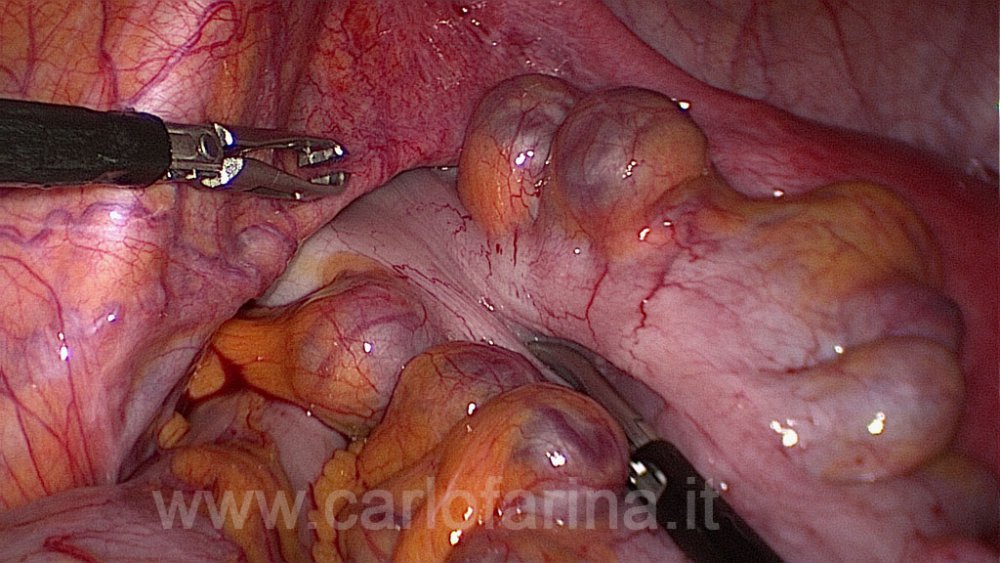
Diverticulas are herniations or little sac-like pouches that protrude from the wall of the colon.
INDEX:
1. WHATS THE MEANING OF DIVERTICULOSIS AND DIVERTICULITIS
2. MEDICAL TREATMENT IN ACUTE DIVERTICULITIS
2.1 DIETARY ADVICE IN DIVERTICULOSIS.
2.2 DIETARY ADVICE IN DIVERTICULITIS.
3. SURGICAL TECHNIQUES
3.1 COLON RESECTION
3.2 TWO STEPS SURGICAL INTERVENTION
1. WHAT'S THE MEANING OF DIVERTICULOSIS AND DIVERTICULITIS Diverticula are herniation or protrusion of the inner layers of the colon( mucosa and submucosa), through the muscular coats of the colon. Diverticular size can varies from few millimiters to many centimeters and are mainly situated in the final part of the colon, the sigmoid. The presence of multiple diverticular of the colon cause a disease called Divericulosis. Currently it is found that diverticular disease affect about 50% of individuals over 60 years of age and it is related with age: at 40 years of age it affect only 10 percent of individuals while it is calculated that at 80 years it affect 80%of person. It is not a congenital diseas but it is acquired and is strictly related to diet fiber intake. In fact the high frequency of diverticular disease in westernized countries and in Japain has resulted from consumption of a diet low in cereal fiber by an aging population. The most common site of diverticula is the sigmoid , involved in 95% of cases.
Uninflamed diverticula clinically represent a Diverticulosi.
The diverticula sacs herniate the colonic wall in the same site were the arteries of the colon pass. This represents an important factor in the causation of hemorrhage in patients with uninflamed diverticula.
Often the diverticulosis is asymptomatic and is an occasional X-ray report or an Endoscopic finder.
The inflamation of the diverticula is Called DIVERTICULITIS. Clinical manifestation include Abdominal pain more frequently on the lower left quadrant, Fever, Increase of White cell ( Leucocithosis), Palpable abdominal mass , haemorrage. During every hepisode of diverticulitis i
Diverticulosis is not a symptom and is an occasional finding discovered during an endoscopic examination or an opaque Rx-Clisma.
Inflammation of the amusements identifies a picture called: Diverticolitis.
Diverticulitis is an acute event characterized by: abdominal pain, fever, increased white blood cells, presence of palpable abdominal masses, bleeding.
During each episode of diverticulitis, abdominal adhesions develop with the possibility of colon-bladder abscesses and fistulas which are communications between the colon and the bladder.
2. MEDICAL THERAPY IN ACUTE DIVERTICULTS
Attack therapy is generally medical, possibly with hospitalization, administration of vein fluids, fasting, broad spectrum antibiotics until the picture improves.
So you will need to follow a specific diet and take specific antibiotics for the intestine, so-called improperly disinfecting intestines. These will be taken every month for 5 to 7 days.
Fundamental will be an abundant flow of liquids associated with abundant fiber intake.
The fibers not only divert diverticulitis but prevent the formation of diverticulas.
In countries where dietary fiber is abundant as in many areas of Africa, residents do not know the colon diverticitis and colon cancer is very rare.
Strangely the diet in simple diverticulitis and acute diverticulitis are very different: while in the simple diverticulosis it is necessary to have an adequate supply of fibers with the feeding in the acute diverticulitis the fibers are harmful, in fact a liquid diet is advised and then pass to a semi-solid, but without fibers.
2.1. FOOD ADVICE IN CASE OF DIVERTICULOSIS
• Prefer fiber-rich foods, which are accompanied by abundant fluid intake (non-carbonated water).
If necessary, supplement your diet with dietary fiber supplements (psyllium, bran ...), but avoid using laxatives.
• Consume a generous breakfast.
• Increase physical movement (jogging, fast pace, cyclists, etc.).
2.2. FOOD ADVICE IN CASE OF DIVERTICOLITE
• Abolish spices, spicy foods (pepper, pepper, nutmeg), alcoholic beverages, carbonated beverages, tea (admittedly dishonest ones), coffee (admitted that decaffeinated) and chocolate.
• Reduce or even eliminate milk consumption; However, a good deal of yogurt and dairy products are tolerated (except hot cheeses).
• Avoid oilseeds, legumes, wholegrain cereals and, more generally, food that produces gas, ie meteorizing (champagne, carbonated water, whipped cream, mayonnaise ...).
• Consume fruit without peel and spin (but not smooth, to prevent the food ingrain excessive amounts of air).
• Avoid all vegetables except lettuce.
However, when we are faced with repeated episodes of diverticulitis, abscesses, perforation of the colon, peritonitis or haemorrhage, surgery is required.
3. SURGICAL TECHNIQUES
The intervention consists in resection of the part of colon sick, which is generally sigma.
The current tendency is to perform it laparoscopically: LAPAROSCOPIC COLON RESEARCH.
Sometimes the condition of the colon is so compromised that it is necessary to pack a Temporary Stoma, that is, a preternatural anus with a bag of feces collection that avoids the passage of these on the resected area.
Depending on the severity of the picture, the surgeon can mainly perform two types of operation in one or two times (in extreme cases).
3.1. PRIMARY ANASTOMOSIS RESPONSE
The removal of the diverticular site's colon tract, and the direct suture of the two colon heads in a single procedure like colon polyps and tumors (see)
3.2. TWO TIMES INTERVENTION
Anastomosis without temporary colostomy.
Colon resection deviating the output of the stools on an outer bag.
When the infection and inflammation of the peritoneum and the colon are completed, one to six months in the most severe cases, a second operation is performed to close the stomach and restore the natural continuity of the colon.
Although more complex and not always possible, laparoscopic pathway offers undoubted advantages for the pacient.