Uterine Fibroids, better defined as LEimiomi or Miomi, are benign tumors of the uterus that affect 20% of women
The uterine fibroids, better defined as Leiomioma or Uterus Mioma, is a benign tumor of the uterus affecting about 20% of women over 30 years of age.
The real percentage is probably higher because most women have no symptoms. However, it is known that the black race has an incidence of fibroids three times higher than the white one.
Leiomiomas are caused by abnormal proliferation of a single clone of muscle cells in the uterus under the influence of estrogen, progesterone and other factors.
This is why often fibroids grow during fertile ages and pregnancy then stop and even decrease in volume after menopause.
They are rarely single, often multiple and are located in the uterus in various venues: Intramural: in myometrium.
Sublime: they are facing the outer surface of the uterus.
Subcutaneous: in contact with the endometrial channel in the deepest part of the uterus.
Other types are the Infralegaments that creep into the lumbar support of the uterus and the rarer Parasitics that are detached from the uterus.
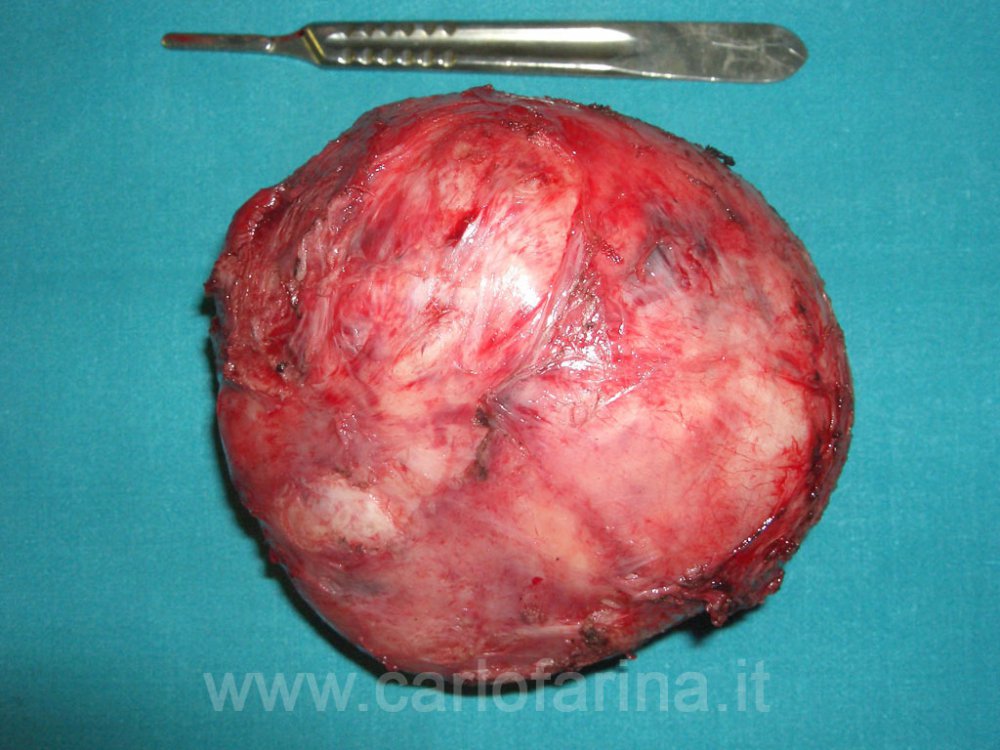
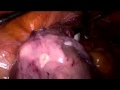
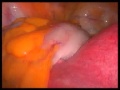
I happened to remove a mass under the groin of a woman which turned out to be a bunch of uterine fibroids completely detached from the uterus. They appear as whitish, hard, and can deform the uterus completely.
The symptoms with which they occur vary depending on the location, number, and size of the fibroids.
Most women report abundant and prolonged menstruation, weight sensation, abdominal swelling and urination frequently.
More rarely, pain during sexual intercourse called Dispareunia, lumbar pain, constipation and urinary retention.
Abundant blood loss can cause anemia. Investigations to be carried out include Ultrasound, Pap test, and Isteroscopy.
In view of a surgical procedure and to confirm the benign nature of the fibroids, an abdominal-pelvic Magnetic Resonance is useful.
If the woman is asymptomatic does not work, otherwise she will be evaluated by the gynecologist to decide if surgery is needed.
SURGICAL TECHNIQUES
1) MIOMECTOMIA:
Removal of myomas.
It can be executed by:
A) LAPAROTOMICS: Through a horizontal abdominal incision as in Caesarean section.
GENERAL INFORMATION FOR THE PATIENT AFTER AFTER INTERVENTIONS OF URBAN FIBROIDS DIRECTION OF Dr. Carlo Farina
The surgery was performed in general or peripheral anesthesia, practicing an incision over the pubis. Usually the hospitalization is 3 days.
The wounds are closed with internal spots that spontaneously re-absorb (there are no spots on the skin) except the wound from which drainage drain (if positioned) where there is only one point and are protected by some waterproof patches that allow To be able to shower after the third day.
You have already initiated a painkiller therapy that will continue to stay at doses and fixed times for three days, then only on need.
It is advisable to wait 4-5 days to drive. During the postoperative period, the patient can perform a regular life.
The cycle generally resumes with small irregularities.
In some cases, you may decide to put the uterus rest for a few months by administering drugs that block the menstrual cycle, which then resumes without consequences.
Any pregnancy should be started after a period of 6 months to 1 year after surgery and after a gynecological examination.
For the first 15 days you will notice an abdominal swelling, which then disappears.
It should be lighter, drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day until regularization of the intestinal function.
In the case of constipation, you may take a mild laxative after the third day (LAEVOLAC: 1 or 2 sachets per day).
The patient may, but not necessarily observe one of the following situations:
- Pain, of a modest extent at the level of the wounds, especially the umbilical and the overweight.
They diminish intensity and disappear in about seven days.
They are well controlled by painkillers.
Dark vaginal discharge: especially for myomas penetrating deep into the uterus.
They run out of the sun for 1 to 2 weeks. Use vaginal lavage. -Any drop of blood on dressings.
- Fever (up to 38 ° C without tremors or chills):
The normal reaction of the body to stress, and disappears in about 7 days (possibly TACHIPIRINA 500 mg - 1 Cp).
Such situations are normal and foreseen and should not be a concern.
Otherwise the patient will need to alert the surgical team promptly.
B) LAPAROSCOPIC:
Removal of myomials by the use of optics through three small abdominal incisions.
C) SINGLE INCISION LAPAROSCOPE:
As before but through a single umbilical engraving.
D) Hysteroscopic: for myomies submissive. It is performed by specialized gynecologists.
2) EMBOSSATION of uterine arteries:
In cases where fibroids can not be removed without sacrificing the entire uterus in premenopausal women who wish to retain the uterus. It is performed by radiologists.
3) TOTAL OR SUBTOTAL ISTERECTOMY:
It consists in removing everything (total hysterectomy) or most of the uterus, saving the neck, that portion of the uterus that looks into the vagina (subtotal hysterectomy) and can be performed by:
A) LAPAROTOMICS:
Through a horizontal incision as in Caesarean section.
B) LAPAROSCOPIC:
Through three small abdominal incisions with the usom of an optic.
C) SINGLE INCISION LAPAROSCOPE:
As before but using a single abdominal incision.
GENERAL INFORMATION FOR THE PATIENT AFTER REMOVAL OF THE UTERUS by Dr. Carlo Farina
(LAPAROTOMIC TOTAL HYSTERECTOMY or SUB-TOTAL HYSTERECTOMY )
The operation was performed under general anesthesia, making an incision over the pubis. Generally the hospitalization is 3-5 days. It has no external stitches to be removed. The wounds are closed with internal stitches that reabsorb spontaneously and are protected by some waterproof patches that allow you to shower after the third day with all the dressing. After the shower, replace only the external patch. After 7-10 days from the operation it will make the first dressing and will be given any other instructions. We recommend the use of a post-operative elastic bandage, to use day and night for 5 days then only during the day for the first month. Although it is indicated to move quietly, walk and make stairs, avoid efforts for a month.
You have already started a pain-relieving therapy that will continue at home in case of need. To drive it is recommended to wait 4-5 days. In the postoperative period you will have a regular life. For the first 2-3 weeks you could see abdominal swelling, which subsequently disappears. It will have to favor a light feeding, drink at least 2 liters of liquids a day, until the regularization of the intestinal functions. In the case of constipation, you may take a mild laxative after the third day (LAEVOLAC: 1 or 2 Cucch per day). After a total hysterectomy, avoid sexual intercourse for about 6 weeks. After a Subtotal Hysterectomy (in which the neck of the uterus was left), it only takes 4 weeks. If you still had your period and had a hysterectomy with ovariectomy, you will experience the typical symptoms of menopause: hot flashes, dry skin and vagina and also signs of depression, anxiety and decreased sexual desire. The hormones that were supposed to secrete the ovaries could be replaced by a therapy that could be prescribed by your Gynecologist who could also advise you to use lubricating creams or gels to resolve vaginal dryness.
The patient may, but not necessarily observe one of the following situations: •-minor pains, sometimes a pang, at the level of the wound, especially at the sides and during the efforts. They decrease in intensity and disappear in about 15 days. They're well controlled by painkillers.
• Dark Vaginal discharge. They run out of themselves in 1 – 3 weeks. Useful vaginal Lavande.
•-a few drops of blood on medication.
• Fever (up to 38 °c without tremors or chills): it is the normal reaction of the organism to the operative stress, and it disappears in about 7 days (possibly: TACHIPIRINA 500 mg-1 Cp).
Such situations are normal and expected and should not arouse any concern. Otherwise the patient should promptly alert the surgical team.