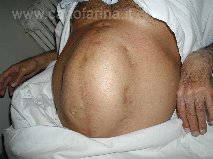
The Ventral Incisional Abdominal wall hernia is an acquired hernia that occur in conseguence of a breaking of the suture of the two margin of the muscular abdominal wall of the previous surgery. Therefore it occurs ONLY in the areas of the abdomenalready undergoing surgery. This can occur even many years after an abdominal surgical operation and expecially under the ombelicus.
An incisional hernia can occur even after a laparoscopy in the site of introduction of the trocar ( the trocar is a little device cilindric the is adopted to introduce the laparoscopic instruments in the abdomen). The only therapy for the incisional hernia is surgical. If not operated, it can be complicated as for any hernia with an intestinal obstruction.
Generally I prescribe an Abdominal CT scan to visualize with more precision the characteristics of the entrance of the laparocele and therefore for a better programming of the intervention.
Surgical technique:
1. POSTOPERATIVE VENTRAL HERNIA REPAIR WITH AN OPEN TECNIQUE
2. LAPAROSCOPYC POSTOPERATIVE VENTRAL HERNIA REPAIR
3. ROBOTIC POSTOPERATIVE VENTRAL HERNIA REPAIR
1. POSTOPERATIVE VENTRAL HERNIA REPAIR WITH AN OPEN TECNIQUE
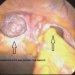
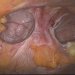
It consists in incising the previous scar, isolating the laparocele sac and possibly checking the vitality of its contents.
Reduce the contents of the incision in the abdomen.
Apply a net that is anchored to the sound wall with series of points or titanium clips.
Close the abdominal wall by placing one or two suction drainage tubes.
Suture the skin with intradermal points, not visible on the skin.
2. LAPAROSCOPYC POSTOPERATIVE VENTRAL HERNIA REPAIR
3. ROBOTIC POSTOPERATIVE VENTRAL HERNIA REPAIR
It consists in introducing the inside of the abdomen always using the laparoscopic technique but with the help of the ROBOT. the surgery in itself is similar to the laparoscopic one, but the precision of the Robot allows to have advantages:
- The movements of the robotic instruments are extremely precise.
- The instruments can be articulated, that is, they reproduce exactly the movements of the hand and wrist and in this way allow to perform with millimeter precision the separation of the various planes in which to store the mesh, or to detach the adhesions greatly reducing the risks of damage to the intestine.
- The intervention is even less invasive than laparoscopy and both hospitalization and discomfort in the postoperative are greatly reduced
The postoperative course reproduces the Laparoscopic one although patients will have a faster recovery than any other technique.